The Genetic Code Is Best Described as
In a eukaryotic cell that is going to make a protein used to regulate glycolysis translation will take place. Biology 22062019 0400 deee12345.

Characteristics Of The Genetic Code A Level Biology Revision Notes
The genetic code is described as what.

. DNA molecules condense to form chromosomes during certain stages of the cell cycle. The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material DNA or RNA sequences is translated into proteins amino acid sequences by living cells. This genetic information is DNA a double-stranded molecule made of strings of nucleotides.
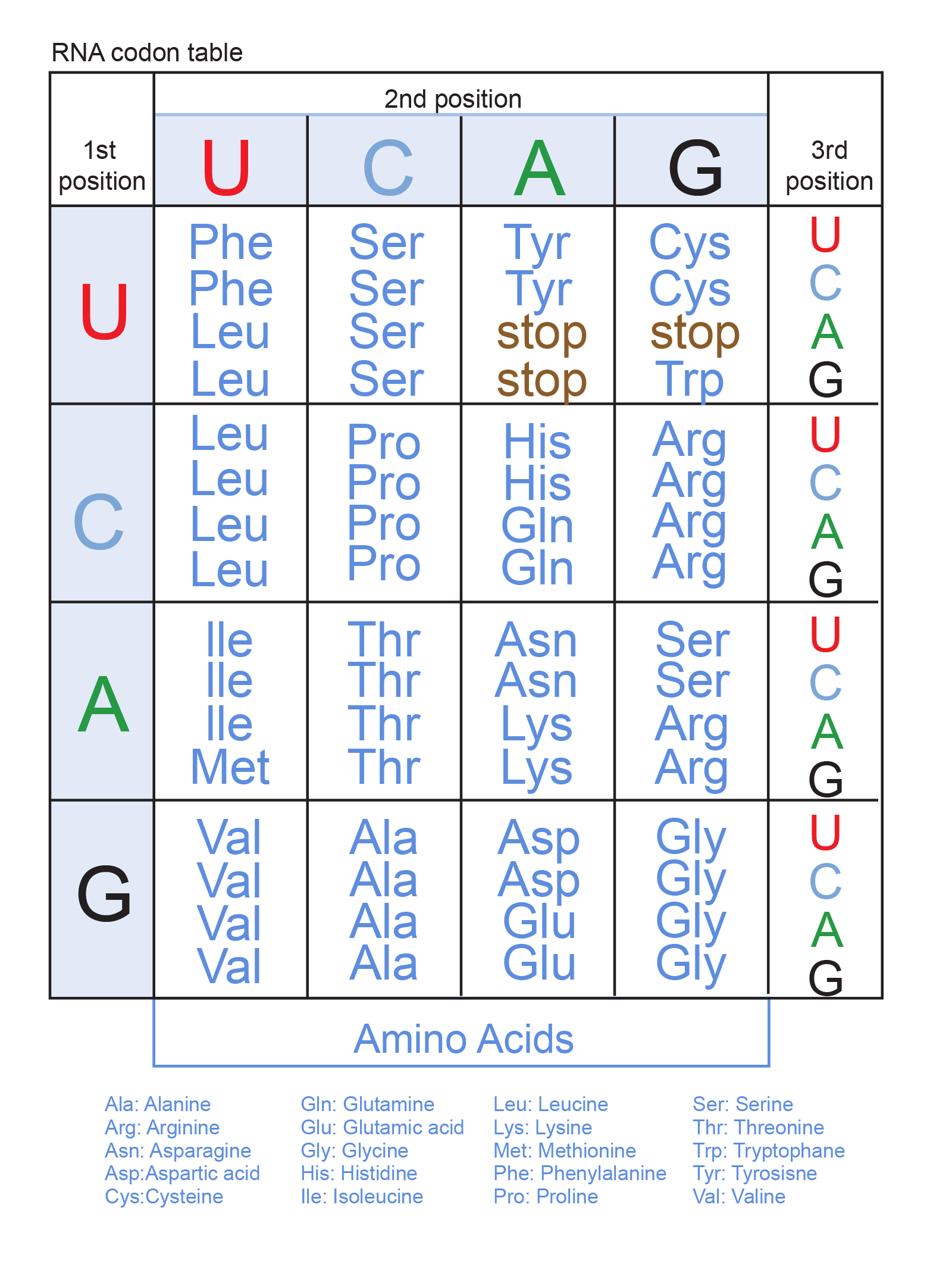
1 codon 1 amino acid B. The main evolutionary novelty implied by the transition from the early to the universal code. Under normal circumstances a given codon encodes one and only one amino acid.
The distribution of related animals and plants across the world. A sequence of three bases is called and codon and this represents one amino acid in the polypeptide. Nirenberg and Johann Matthaei conducted experiments on protein synthesis using synthetic RNA.
The flow of information in a cell is best described as DNA is transcribed to mRNA the information in mRNA is then translated into a sequence of amino acids in a ribosome. The instructions in a gene that tell the cell how to make a specific protein. The four nucleotide bases are adenosine thymidine cytidine and guanosine.
Holley and Har Gobind Khorana for deciphering the genetic code. Which best describes the storage of the genetic code. The simplest variant of extant codes is the vertebrate mitochondrial genetic code that mainly for this reason has been proposed as a model of the predecessor of the universal LUCA code.
Each genes code combines the four chemicals in various ways to spell out three-letter. View the full answer. O ambiguous but not redundant.
How water is moving through the ecosystem. They stand for the chemicals adenine A cytosine C guanine G and thymine T respectively that make up the nucleotide bases of DNA. The genetic code once thought to be identical in all forms of life has been found to diverge slightly in certain organisms and in the mitochondria of some eukaryotes.
The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material DNA or RNA sequences is translated into proteins amino acid sequences by living cells. Three bases form an amino acid also known as a codon. O redundant but not ambiguous.
Biology 22062019 0800 ramseynikki87. Genetic code is redundant because. A DNA molecule is a segment of a gene a gene makes up a chromosome a chromosome is inside a cell and a cell is contained within a nucleus.
What is the flow of genetic information from DNA to protein. 6 codon1 amino acid D. The early code the second milestone from the right in figure 4.
Redundant but not ambiguous. DNA is considered a universal genetic code because every known living organism has genes made of DNA. Neither ambiguous nor redundant.
The genetic code is the code our body uses to convert the instructions contained in our DNA the essential materials of life. Ambiguous but not redundant. A gene is a segment of DNA a condensed DNA molecule makes up a chromosome a chromosome is inside a nucleus and a nucleus is contained within a cell.
This is considered to be nonoverlapping and comma-less. Although it is a redundant code it is not an ambiguous code. Redundant in prokaryotes but ambiguous in eukaryotes.
Which of the following best describes the degeneracy of the genetic code. It is the sequence of bases on the DNA strand that codes for proteins. Basically every three pieces of DNA becomes one amino acid.
Which best describes the genetic code Other questions on the subject. The genetic code is the instruction that a gene uses to tell a cell how to make a specific protein. A C G and T are the letters of the DNA code.
The genetic code is a set of rules defining how the four-letter code of DNA is translated into the 20-letter code of amino acids which are the building blocks of proteins. He won the Nobel prize in 1968 along with Robert W. A second theory is the capture hypothesis in which the moon formed elsewhere in the solar system and the.
Organism differ according to the arrangement of the nucleotide bases. Genetic Code Definition. Every living organism uses that same system.
The genetic code is a degenerate code which means that there is redundancy so that most amino acids are encoded by more than one triplet combination codon. Both ambiguous and redundant. UUU was the first code to be deciphered which was for phenylalanine.
Two popular theories of the moons origin include the sister world hypothesis which states that the moon formed from the same materials as the earth near enough to the earth that they fell into orbit around each other. These nucleotide sequences form genes which are segments of DNA that code for proteins. The genetic code is called a universal code because all known organisms use the same four nucleotide bases.
The amino acid it becomes depends upon that three-letter sequence which is called a codon. Marshall Nirenberg discovered the genetic code. The genetic code is described as degenerate because often more than one codon codes for the same amino acid.
DNA gene 3-5 DNA template strand transcription mRNA 5-3 triplet code words translation on. It is typically discussed using the codons found in mRNA as mRNA is the messenger that carries information from the DNA to the site of protein synthesis. The earths moon is unusually large.
The genetic code is best described as O both ambiguous and redundant. The genetic code is best described as a. None of the above.
1 codon 6 amino acid C.
Comments
Post a Comment