Explain the Different Steps of Krebs Cycle
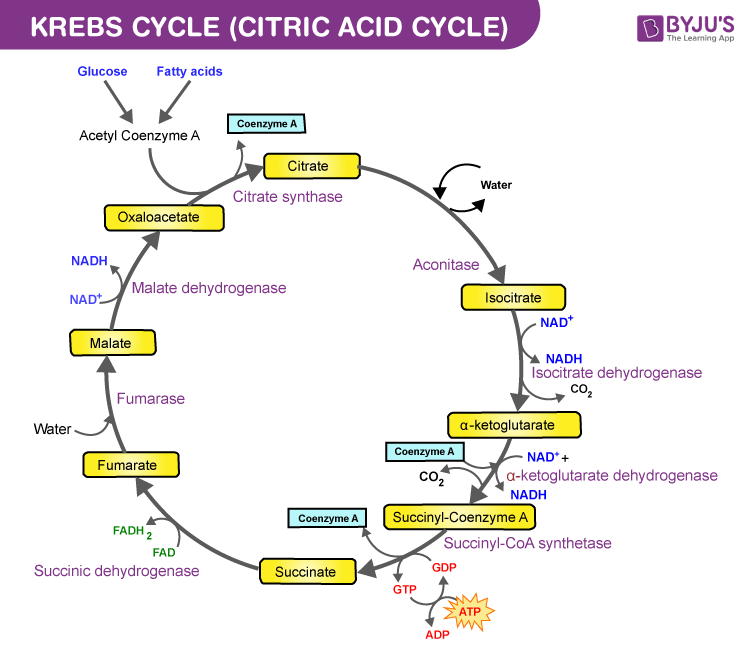
These carriers transfer that energy to oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria. Acetyl-CoA is transformed into Citrate via citrate synthase releasing water as a byproduct it also uses oxaloacetate which is regenerated at the end.
Krebs Cycle Or Citric Acid Cycle Steps Products Significance
CoA is bound to a sulfhydryl group -SH and diffuses away to.
. Coenzyme A is released so that it can bring another molecule of acetate to the Krebs Cycle. The first step is a condensation step combining the two-carbon acetyl group from acetyl CoA with a four-carbon oxaloacetate molecule to form a six-carbon molecule of citrate. Its purpose is to collect high-energy electrons for use in the electron transport chain reactions.
A carboxyl group i s removed as CO 2. Name one step in which carbon dioxide is produced. The first step is the condensation of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetate 4C to form citrate 6C coenzyme A is released.
The enzyme aconitase catalyses this reaction. Krebs cyclelink reaction produces reduced coenzyme. This is the decarboxylation part.
In the second step citrate is converted into its isomer isocitrate. Formation of a 5-carbon molecule. -Krebs cycle so the acetyl Co A enters the inner membrane of the mitochondria and begins the Krebs cycle also known as the citric acid cycle Where it bonds with Oxaloacetate to form Citric Acid and through a series of complex steps produces 2 ATP 6 NADH 4 CO2 and 2FADH another electron carrier per glucose molecule since two Acetyl CoAs.
The 2C Acetyl molecule is broken down into. The following steps occur. This is a two-step process.
So for every 1 pyruvate molecule added the Krebs cycle will produce. The reaction is catalyzed by citrate synthase. Then the remaining 2-carbon part is oxidized by NAD.
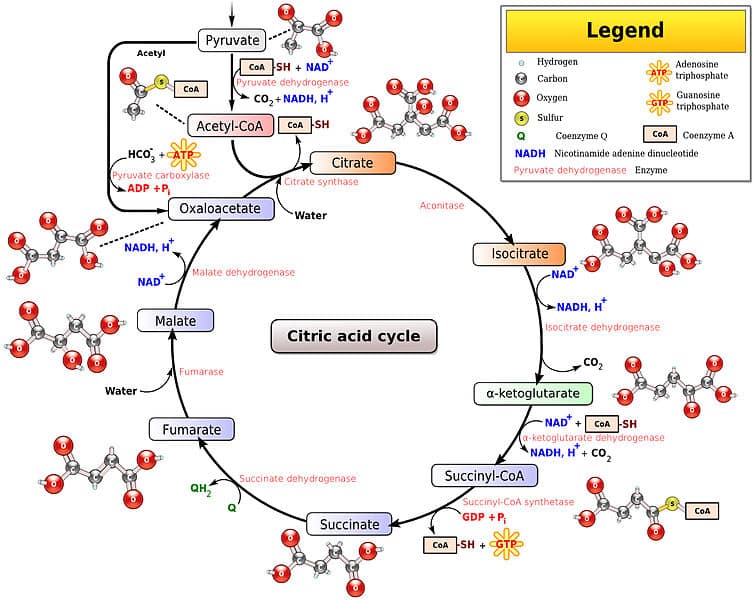
How many glucose molecules can undergo cellular respiration when 13 O2 molecules are available to react. The Krebs cycle is the next step of cellular respiration but before the Krebs cycle takes place we need another step called Oxidative Decarboxylation which has to convert pyruvate into acetyl-CoA. A conitase 3.
It is an eight-step process. This is a very short step in between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. List the steps of the Krebs cycle and the products it creates.
Acetyl CoA a 2-carbon molecule combines with oxaloacetate a 4-carbon molecule. Citrate is converted to its isomer isocitrate. Acetyl CoA two carbon molecule joins with oxaloacetate 4 carbon molecule to form citrate 6 carbon molecule.
In the first step of the citric acid cycle acetyl joins with a four-carbon molecule oxaloacetate releasing the group and forming a six-carbon molecule called citrate. The Krebs cycle also called the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic cycle is the first step of aerobic respiration in eukaryotic cells. The citric acid cycle is also known as the Krebs cycle.
The results are shown in the graph. The first step is to put energy into the system. The steps of the Krebs cycle are as follows.
Krebs Cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. Citrate is produced in this step when Acetyl CoA adds its two-carbon acetyl group to oxaloacetate. The biochemical pathway of aerobic respiration involves a number of different steps.
The Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. NAD gets reduced to NADH. The third step involves oxidation of isocitrate.
Krebs Cycle Step by Step. Citrate is converted to its isocitrate an an isomer of citrate by the removal of one water molecule and adding the another. How is photosynthesis related to changes in the.
Citrate synthatase to put energy into system 2. 1 the decarboxylation of pyruvate represents the first of six decarboxylations within this reaction cycle one for each of the six carbon atoms present in the initial substrate glucose facilitating its complete oxidation. An enzyme combines the 2-carbon acetate molecules with a 4-carbon acid called oxaloacetate to form a 6-carbon acid called citrate 3.
Pyruvate is needed in order to create acetyl CoA. Steps involved in Krebs cycle. The combination forms the six carbon acid called citric acid as the first product is citric acid so the krebs cycle is also called as citric acid cycle.
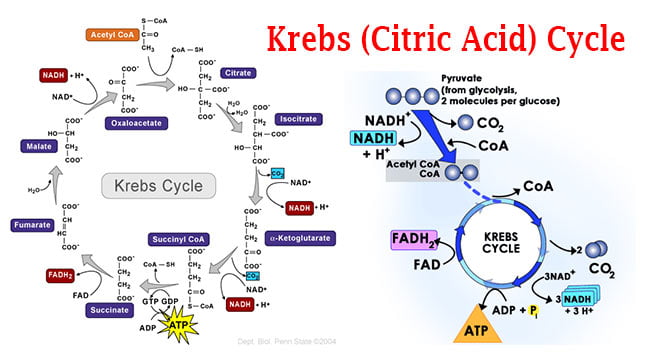
Isocitrate undergoes dehydrogenation and. The FADH 2 and NADH generated in the Krebs cycle donate their electrons to oxygen through various electron carriers via the electron transport chain in a process known as oxidative phosphorylation. Purpose of this cycle is to generate electron carriers or reduction carriers.
3 molecules of NADH. The first step is the condensation of acetyl CoA with 4-carbon compound oxaloacetate to form 6C citrate. It takes place over eight different steps.
The transformation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA. The Krebs cycle is known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle as well. The Krebs cycle takes place in the matrix of mitochondria under aerobic conditions.
Where acetate enters the Krebs Cycle 2. Citrate is converted to isocitrate an isomer of citrate Step 3. The 3-carbon pyruvate molecule made in glycolysis loses a carbon to.
The various enzymes involved in different steps are. Citrate first loses a water molecule and then gains one to form isocitrate. Citrate is turned to its isomer isocitrate.
Aconitase reacts with the aconitate to form D-isocitrate which I believe requires a water molecule. 2 molecules of CO 2. When is carbon dioxide released during cellular respiration.
Refer to exam q in book Describe and explain the relationship between light. The reaction takes place in the mitochondrial matrix. 1 molecule of GTP.
2 the high energy electrons stored within the eight NADH molecules generated will used later to. 1 molecule of FADH 2. This cycle occurs following glycolysis.
ATP is produced in the Krebs cycle. Citrate is converted into a 5-carbon molecule called alpha-ketoglutarate. Citrate is then transformed into cis-Aconitate via aconitase.
Krebs Cycle Steps Step 1. 2 x CO2 molecules waste product releasing energy to build up 2ATP molecules releasing H carried by NAD red NAD and FAD red FAD to generate more ATP via oxidative phosphorylation. There are two things to note from this initial step of the Krebs cycle.
How can ATP be used to lower the body tempgive a specific example 5. During the steps of the cycle two molecules of CO 2 are released in addition to 3 more molecules of NADH one of FADH 2 and one of GTP. In the second step citrate gets converted to isocitrate an isomer of citrate.
A molecule of carbon dioxide is released leaving behind a five-carbon molecule ɑ-ketoglutarate. The Krebs cycle involves converting this acetyl CoA into carbon dioxide. Formation of a 6-carbon molecule.
Isocitrate is oxidised to alpha-ketoglutarate a five carbon.

The Tca Cycle Steps Krebs Cycle Teachmephysiology
Krebs Citric Acid Cycle Steps By Steps Explanation Microbiology Info Com

The Citric Acid Cycle Cellular Respiration Article Khan Academy
ReplyDeleteThank You for sharing such a wonderful blog, it is very useful.nursery admission in bangalore